Anemia prevalence: an rdhs
example
OJ Watson, Jeff Eaton
2018-09-24
Source:vignettes/anemia.Rmd
anemia.RmdAnemia is a common cause of fatigue, and women of childbearing age
are at particularly high risk for anemia. The package rdhs
can be used to compare estimates of the prevalence of any anemia among
women from Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) conducted in Armenia,
Cambodia, and Lesotho.
Using calculated indicators from STATcompiler
Anemia prevalence among women is reported as a core indicator through
the DHS STATcompiler (https://www.statcompiler.com/). These indicators can be
accessed directly from R via the DHS API with the function
dhs_data().
Query the API for a list of all StatCompiler indicators, and then
search the indicators for those that have "anemia" in the
indicator name. API calls return data.frame objects, so if
you prefer to use data.table objects then convert
afterwards, or we can set this up within our config using
set_rdhs_config.
library(rdhs)
set_rdhs_config(data_frame = "data.table::as.data.table")
indicators <- dhs_indicators()
tail(indicators[grepl("anemia", Label), .(IndicatorId, ShortName, Label)])## IndicatorId ShortName Label
## 1: CN_ANMC_C_SEV Severe anemia (<7.0 g/dl) Children with severe anemia
## 2: AN_ANEM_W_ANY Any Women with any anemia
## 3: AN_ANEM_W_MLD Mild Women with mild anemia
## 4: AN_ANEM_W_MOD Moderate Women with moderate anemia
## 5: AN_ANEM_W_SEV Severe Women with severe anemia
## 6: AN_ANEM_M_ANY Any anemia Men with any anemiaThe indicator ID "AN_ANEM_W_ANY" reports the percentage
of women with any anemia. The function dhs_data() will
query the indicator dataset for the value of this indicator for our
three countries of interest. First, use dhs_countries() to
query the list of DHS countries to identify the DHS country code for
each country.
countries <- dhs_countries()
dhscc <- countries[CountryName %in% c("Armenia", "Cambodia", "Lesotho"), DHS_CountryCode]
dhscc## [1] "AM" "KH" "LS"Now query the indicators dataset for the women with any anemia indicator for these three countries.
statcomp <- dhs_data(indicatorIds = "AN_ANEM_W_ANY", countryIds = dhscc)
statcomp[,.(Indicator, CountryName, SurveyYear, Value, DenominatorWeighted)]## Indicator CountryName SurveyYear Value DenominatorWeighted
## 1: Women with any anemia Armenia 2000 12.4 6137
## 2: Women with any anemia Armenia 2005 24.6 6080
## 3: Women with any anemia Armenia 2016 13.4 5769
## 4: Women with any anemia Cambodia 2000 58.8 3634
## 5: Women with any anemia Cambodia 2005 46.7 8219
## 6: Women with any anemia Cambodia 2010 44.4 9229
## 7: Women with any anemia Cambodia 2014 45.4 11286
## 8: Women with any anemia Lesotho 2004 32.9 3008
## 9: Women with any anemia Lesotho 2009 26.3 3839
## 10: Women with any anemia Lesotho 2014 27.3 3297
ggplot(statcomp, aes(SurveyYear, Value, col=CountryName)) +
geom_point() + geom_line()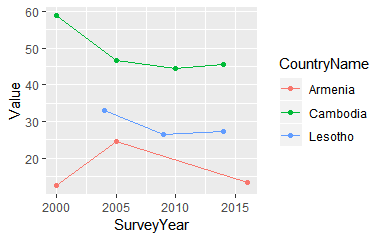
Analyse DHS microdata
Identify surveys that include anemia testing
The DHS API provides the facility to filter surveys according to
particular characteristics. We first query the list of survey
characteristics and identify the SurveyCharacteristicID
that indicates the survey included anemia testing. The first command
below queries the API for the full list of survey characteristics, and
the second uses grepl() to search
SurveyCharacteristicNames that include the word
‘anemia’.
surveychar <- dhs_survey_characteristics()
surveychar[grepl("anemia", SurveyCharacteristicName, ignore.case=TRUE)]## SurveyCharacteristicID SurveyCharacteristicName
## 1: 15 Anemia questions
## 2: 41 Anemia testingThe SurveyCharacteristicID = 41 indicates that the
survey included anemia testing. Next we query the API to identify the
surveys that have this characteristic and were conducted in our
countries of interest.
surveys <- dhs_surveys(surveyCharacteristicIds = 41, countryIds = dhscc)
surveys[,.(SurveyId, CountryName, SurveyYear, NumberOfWomen, SurveyNum, FieldworkEnd)]## SurveyId CountryName SurveyYear NumberOfWomen SurveyNum FieldworkEnd
## 1: AM2000DHS Armenia 2000 6430 203 2000-12-01
## 2: AM2005DHS Armenia 2005 6566 262 2005-12-01
## 3: AM2016DHS Armenia 2016 6116 492 2016-04-01
## 4: KH2000DHS Cambodia 2000 15351 140 2000-07-01
## 5: KH2005DHS Cambodia 2005 16823 257 2006-03-01
## 6: KH2010DHS Cambodia 2010 18754 310 2011-01-01
## 7: KH2014DHS Cambodia 2014 17578 464 2014-12-01
## 8: LS2004DHS Lesotho 2004 7095 256 2005-01-01
## 9: LS2009DHS Lesotho 2009 7624 317 2010-01-01
## 10: LS2014DHS Lesotho 2014 6621 462 2014-12-01Finally, query the API identify the individual recode (IR) survey datasets for each of these surveys
datasets <- dhs_datasets(surveyIds = surveys$SurveyId, fileType = "IR", fileFormat="flat")
datasets[, .(SurveyId, SurveyNum, FileDateLastModified, FileName)]## SurveyId SurveyNum FileDateLastModified FileName
## 1: AM2000DHS 203 October, 05 2006 14:22:40 AMIR42FL.ZIP
## 2: AM2005DHS 262 February, 02 2010 10:38:12 AMIR54FL.zip
## 3: AM2016DHS 492 September, 21 2017 16:10:15 AMIR71FL.ZIP
## 4: KH2000DHS 140 October, 08 2007 12:31:53 KHIR42FL.zip
## 5: KH2005DHS 257 October, 18 2011 13:53:19 KHIR51FL.zip
## 6: KH2010DHS 310 October, 26 2011 11:11:07 KHIR61FL.ZIP
## 7: KH2014DHS 464 July, 28 2017 10:58:10 KHIR73FL.ZIP
## 8: LS2004DHS 256 July, 31 2007 13:14:31 LSIR41FL.ZIP
## 9: LS2009DHS 317 November, 10 2015 10:51:05 LSIR61FL.ZIP
## 10: LS2014DHS 462 June, 14 2016 11:35:19 LSIR71FL.ZIPDownload datasets
To download datasets we need to first log in to our DHS account, by
providing our credentials and setting up our configuration using
set_rdhs_config(). This will require providing as arguments
your email and project for which you want to
download datasets from. You will then be prompted for your password. You
can also specify a directory for datasets and API calls to be cached to
using cache_path. In order to comply with CRAN, this
function will also ask you for your permission to write to files outside
your temporary directory, and you must type out the filename for the
config_path - “rdhs.json”. (See introduction
vignette for specific format for config, or
?set_rdhs_config).
## set up your credentials
set_rdhs_config(email = "jeffrey.eaton@imperial.ac.uk",
project = "Joint estimation of HIV epidemic trends and adult mortality")After this the function get_datasets() returns a list of
file paths where the desired datasets are saved in the cache. The first
time a dataset is accessed, rdhs will download the dataset
from the DHS program website using the supplied credentials.
Subsequently, datasets will be simply be located in the cached
repository.
datasets$path <- unlist(get_datasets(datasets$FileName))## Logging into DHS website...## Creating Download url list from DHS website...Identify survey variables
Anemia is defined as having a hemoglobin (Hb) <12.0 g/dL for non-pregnant women or Hb <11.0 g/dL for currently pregnant women1. To calculate anemia prevalence from DHS microdata, we must identify the DHS recode survey variables for hemoglobin measurement and pregnancy status. This could be done by consulting the DHS recode manual or the .MAP files accompanying survey datasets. It is convenient though to do this in R by loading the first individual recode dataset and searching the metadata for the variable names corresponding to the hemoglobin measurement and pregnancy status.
head(search_variable_labels(datasets$FileName[10], "hemoglobin")[,1:2])## variable
## 1 v042
## 2 v452c
## 3 v453
## 4 v455
## 5 v456
## 6 hw52_1
## description
## 1 Household selected for hemoglobin
## 2 Read consent statement - hemoglobin
## 3 Hemoglobin level (g/dl - 1 decimal)
## 4 Result of measurement - hemoglobin
## 5 Hemoglobin level adjusted for altitude and smoking (g/dl - 1 decimal)
## 6 Read consent statement - hemoglobinVariable v042 records the household selection for
hemoglobin testing. Variable v455 reports the outcome of
hemoglobin measurement and v456 the result of altitude
adjusted hemoglobin levels.
##
## not selected selected
## 3203 3418##
## measured not present
## 3349 2
## refused other
## 35 8
## no measurement found in household missing
## 0 24
summary(ir$v456)## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. NA's
## 24.0 118.0 130.0 145.6 141.0 999.0 3203Variable v454 reports the current pregnancy status used
for determining the anemia threshold.
search_variable_labels(datasets$FileName[1], "currently.*pregnant")[,1:2]## variable description
## 1 v213 Currently pregnant
## 2 v454 Currently pregnant##
## no/don't know yes missing
## 3276 142 0We also keep a number of other variables related to the survey design
and potentially interesting covariates: country code and phase
(v000), cluster number (v001), sample weight
(v005), age (v012), region
(v024), urban/rural residence (v025), and
education level (v106).
vars <- c("SurveyId", "CountryName", "SurveyYear", "v000", "v001", "v005",
"v012", "v024", "v025", "v106", "v042", "v454", "v455", "v456")Extract survey data
datlst <- list()
for(i in 1:nrow(datasets)){
if(file.exists(datasets$path[i])){
print(paste(i, datasets$SurveyId[i]))
ir <- readRDS(datasets$path[i])
ir$SurveyId <- datasets$SurveyId[i]
ir$CountryName <- datasets$CountryName[i]
ir$SurveyYear <- datasets$SurveyYear[i]
datlst[[datasets$SurveyId[i]]] <- ir[vars]
}
}## [1] "1 AM2000DHS"
## [1] "2 AM2005DHS"
## [1] "3 AM2016DHS"
## [1] "4 KH2000DHS"
## [1] "5 KH2005DHS"
## [1] "6 KH2010DHS"
## [1] "7 KH2014DHS"
## [1] "8 LS2004DHS"
## [1] "9 LS2009DHS"
## [1] "10 LS2014DHS"We use rbind_labelled() to combine datasets with
labelled columns. The argument labels describes to combine
variable levels for all datasets for v024 (region) while
providing a consistent set of value labels to be used for
v454 (currently pregnant) for all datasets.
dat <- rbind_labelled(datlst,
labels = list(v024 = "concatenate",
v454 = c("no/don't know" = 0L,
"yes" = 1L, "missing" = 9L)))## Warning in rbind_labelled(datlst, labels = list(v024 = "concatenate", v454 = c(`no/don't know` = 0L, : Some variables have non-matching value labels: v106, v455, v456.
## Inheriting labels from first data frame with labels.
sapply(dat, is.labelled)## SurveyId CountryName SurveyYear v000 v001 v005
## FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
## v012 v024 v025 v106 v042 v454
## FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
## v455 v456 DATASET
## TRUE TRUE FALSE
dat$v456 <- zap_labels(dat$v456)
dat <- as_factor(dat)Data tabulations
It is a good idea to check basic tabulations of the data, especially by survey to identify and nuances Exploratory analysis of variables
## v025
## SurveyId urban rural
## AM2000DHS 3545 2885
## AM2005DHS 4592 1974
## AM2016DHS 3545 2571
## KH2000DHS 2627 12724
## KH2005DHS 4152 12671
## KH2010DHS 6077 12677
## KH2014DHS 5667 11911
## LS2004DHS 1945 5150
## LS2009DHS 1977 5647
## LS2014DHS 2202 4419## v106
## SurveyId no education primary secondary higher missing
## AM2000DHS 5 24 5329 1072 0
## AM2005DHS 7 24 5138 1397 0
## AM2016DHS 5 406 2580 3125 0
## KH2000DHS 4849 8182 2276 44 0
## KH2005DHS 3772 9131 3771 149 0
## KH2010DHS 3203 8796 6141 614 0
## KH2014DHS 2233 7826 6535 984 0
## LS2004DHS 169 4309 2520 97 0
## LS2009DHS 114 3865 3277 368 0
## LS2014DHS 81 2665 3354 521 0## v454
## SurveyId no/don't know yes missing <NA>
## AM2000DHS 6231 199 0 0
## AM2005DHS 5967 158 441 0
## AM2016DHS 5939 177 0 0
## KH2000DHS 3312 296 62 11681
## KH2005DHS 7685 501 212 8425
## KH2010DHS 8906 475 0 9373
## KH2014DHS 10883 663 0 6032
## LS2004DHS 2857 203 0 4035
## LS2009DHS 3740 173 103 3608
## LS2014DHS 3276 142 0 3203## v455
## SurveyId measured not present refused other no measurement found in hh
## AM2000DHS 6137 5 264 24 0
## AM2005DHS 6134 8 294 1 0
## AM2016DHS 5807 11 295 0 0
## KH2000DHS 3666 0 68 0 0
## KH2005DHS 8182 2 185 5 0
## KH2010DHS 9225 9 106 0 0
## KH2014DHS 11390 8 13 2 0
## LS2004DHS 3061 15 377 56 0
## LS2009DHS 3896 1 78 5 0
## LS2014DHS 3349 2 35 8 0
## v455
## SurveyId missing <NA>
## AM2000DHS 0 0
## AM2005DHS 129 0
## AM2016DHS 3 0
## KH2000DHS 3 11614
## KH2005DHS 24 8425
## KH2010DHS 41 9373
## KH2014DHS 133 6032
## LS2004DHS 29 3557
## LS2009DHS 36 3608
## LS2014DHS 24 3203## v454
## v042 no/don't know yes missing <NA>
## not selected 0 0 0 45778
## selected 58796 2987 818 579Calculate anemia prevalence
Create indicator variable for ‘any anemia’. The threshold depends on pregnancy status.
##
## v455 FALSE TRUE
## measured 60847 0
## not present 0 61
## refused 0 1715
## other 0 101
## no measurement found in hh 0 0
## missing 0 422
dat$anemia <- as.integer(dat$v456 < ifelse(dat$v454 == "yes", 110, 120))
dat$anemia_denom <- as.integer(!is.na(dat$anemia))Specify survey design using the survey package.
dat$w <- dat$v005/1e6
des <- svydesign(~v001+SurveyId, data=dat, weights=~w)
anemia_prev <- svyby(~anemia, ~SurveyId, des, svyciprop, na.rm=TRUE, vartype="ci")
anemia_denom <- svyby(~anemia_denom, ~SurveyId, des, svytotal, na.rm=TRUE)
anemia_prev <- merge(anemia_prev, anemia_denom[c("SurveyId", "anemia_denom")])
res <- statcomp[,.(SurveyId, CountryName, SurveyYear, Value, DenominatorUnweighted, DenominatorWeighted)][anemia_prev, on="SurveyId"]
res$anemia <- 100*res$anemia
res$ci_l <- 100*res$ci_l
res$ci_u <- 100*res$ci_u
res$anemia_denom0 <- round(res$anemia_denom)The table below compares the prevalence of any anemia calculated from survey microdata with the estimates from DHS StatCompiler and the weighted denominators for each calculation. The estimates are identical for most cases. There are some small differences to be ironed out, which will require looking at the specific countries to check how their stratification was carried out. (We are hoping to bring this feature in once the DHS program has compiled how sample strata were constructed for all of their studies).
knitr::kable(res[,.(CountryName, SurveyYear, Value, anemia, ci_l, ci_u, DenominatorWeighted, anemia_denom0)], digits=1)| CountryName | SurveyYear | Value | anemia | ci_l | ci_u | DenominatorWeighted | anemia_denom0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armenia | 2000 | 12.4 | 11.7 | 10.6 | 13.0 | 6137 | 6137 |
| Armenia | 2005 | 24.6 | 23.1 | 21.3 | 24.9 | 6080 | 6080 |
| Armenia | 2016 | 13.4 | 13.4 | 11.8 | 15.3 | 5769 | 5769 |
| Cambodia | 2000 | 58.8 | 58.8 | 56.6 | 60.9 | 3634 | 3634 |
| Cambodia | 2005 | 46.7 | 46.7 | 44.9 | 48.5 | 8219 | 8219 |
| Cambodia | 2010 | 44.4 | 44.4 | 42.8 | 46.0 | 9229 | 9229 |
| Cambodia | 2014 | 45.4 | 45.4 | 44.1 | 46.7 | 11286 | 11286 |
| Lesotho | 2004 | 32.9 | 32.7 | 30.5 | 35.1 | 3008 | 2789 |
| Lesotho | 2009 | 26.3 | 25.5 | 23.8 | 27.4 | 3839 | 3839 |
| Lesotho | 2014 | 27.3 | 27.3 | 25.2 | 29.4 | 3297 | 3297 |
ggplot(res, aes(x=SurveyYear, y=anemia, ymin=ci_l, ymax=ci_u,
col=CountryName, fill=CountryName)) +
geom_ribbon(alpha=0.4, linetype="blank") + geom_point() + geom_line()
Regression analysis: relationship between education and anemia
A key use of the survey microdata are to conduct secondary analysis
of pooled data from several surveys, such as regression analysis. Here
we investigate the relationship between anemia prevalence and education
level (v106) for women using logistic regression, adjusting
for urban/rural (v025) and fixed effects for each
survey.
des <- update(des, v106 = relevel(v106, "primary"))
summary(svyglm(anemia ~ SurveyId + v025 + v106, des, family="binomial"))## Warning in eval(family$initialize): non-integer #successes in a binomial
## glm!##
## Call:
## svyglm(formula = anemia ~ SurveyId + v025 + v106, des, family = "binomial")
##
## Survey design:
## update(des, v106 = relevel(v106, "primary"))
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) -1.91019 0.06478 -29.489 < 2e-16 ***
## SurveyIdAM2005DHS 0.82908 0.08086 10.253 < 2e-16 ***
## SurveyIdAM2016DHS 0.21583 0.09571 2.255 0.024488 *
## SurveyIdKH2000DHS 2.14550 0.07503 28.596 < 2e-16 ***
## SurveyIdKH2005DHS 1.68112 0.07260 23.155 < 2e-16 ***
## SurveyIdKH2010DHS 1.61671 0.06961 23.224 < 2e-16 ***
## SurveyIdKH2014DHS 1.66621 0.06406 26.011 < 2e-16 ***
## SurveyIdLS2004DHS 1.13997 0.07960 14.322 < 2e-16 ***
## SurveyIdLS2009DHS 0.82962 0.07756 10.696 < 2e-16 ***
## SurveyIdLS2014DHS 0.93593 0.08164 11.464 < 2e-16 ***
## v025rural 0.11625 0.03220 3.610 0.000332 ***
## v106no education 0.15431 0.03845 4.013 6.75e-05 ***
## v106secondary -0.11932 0.02787 -4.282 2.16e-05 ***
## v106higher -0.33508 0.04985 -6.722 4.19e-11 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 0.99451)
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 4The results suggest that anemia prevalence is lower among women with higher education.