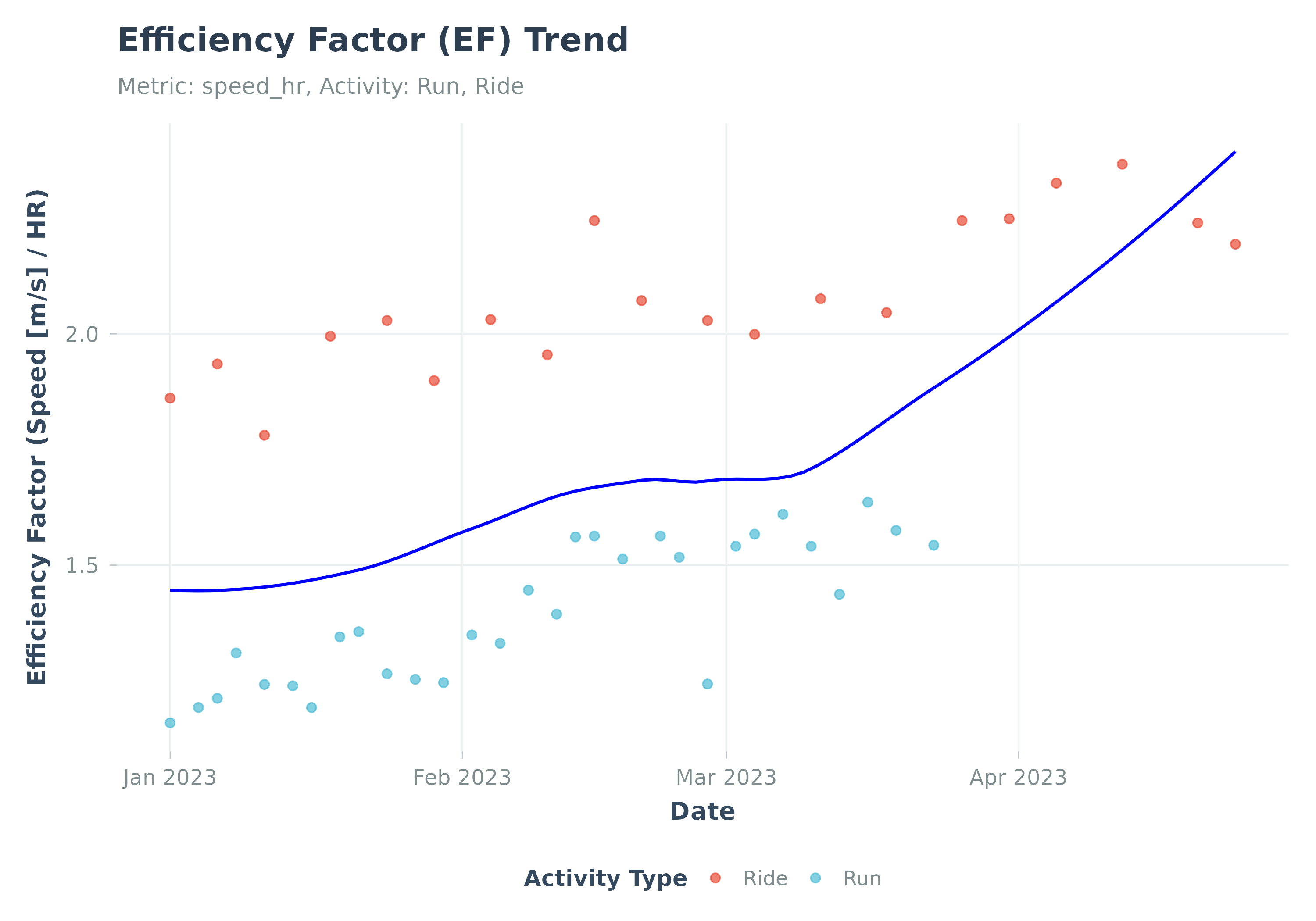
Visualizes the trend of Efficiency Factor (EF) over time.
Usage
plot_ef(
data,
add_trend_line = TRUE,
smoothing_method = "loess",
smooth_per_activity_type = FALSE,
group_var = NULL,
group_colors = NULL,
title = NULL,
subtitle = NULL,
...
)Arguments
- data
A data frame from
calculate_ef(). Must containdate,ef_value, andactivity_typecolumns.- add_trend_line
Add a smoothed trend line (
geom_smooth)? DefaultTRUE.- smoothing_method
Smoothing method for trend line (e.g., "loess", "lm"). Default "loess".
- smooth_per_activity_type
Logical. If
TRUEandadd_trend_line = TRUE, draws separate trend lines for each activity type. DefaultFALSE(single trend line for all data). Note: this parameter only applies whengroup_var = NULL. Whengroup_varis set, smoothing is always done per group and this parameter is ignored with a warning.- group_var
Optional. Column name for grouping/faceting (e.g., "athlete_id").
- group_colors
Optional. Named vector of colors for groups.
- title
Optional. Custom title for the plot.
- subtitle
Optional. Custom subtitle for the plot.
- ...
Additional arguments. Arguments
activity_type,ef_metric,start_date,end_date,min_duration_mins,ef_dfare deprecated and ignored.
Details
Plots EF (output/HR based on activity averages).
Best practice: Use calculate_ef() first, then pass the result to this function.